HKCERT CTF Quals 2024 Writeup (Part 2)

This post will cover my solutions for Pigeon Post (2) and 2 mAEStro challenges.
Pigeon Post (2)#
Challenge Analysis#
- This challenge implements a Diffie-Hellman key exchange on 2 entities: Alice and Byron. After the process, both entities agree on a session ke $SK$, which is used as key for AES-CTR for communication phase.
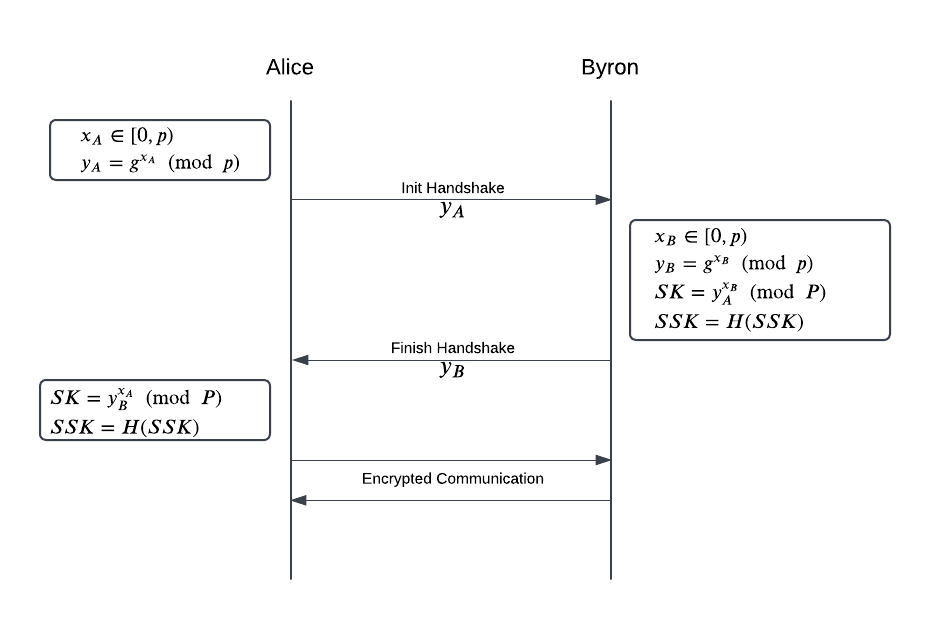
- In communication phase, all messages are encrypted with AES-CTR. Alice and Byron, whose secret is $s_A$ and $s_B$ respectively, have specific responses to different type of messages:
-
Alice:
Received Response what is the flag? I have the secret+ $s_B$the flag is+ $s_A$nice flag!:)too bad...what happened?Other ??? -
Byron:
Received Response done!what is the flag? I have the secret+ $s_B$Prefix: the flag is, suffix:hkcert24{.*}nice flag!Prefix: the flag is, other suffixtoo bad...Other ???
-
Solution#
- In
Pigeon Post (1), we can intercept the key exchange phase and thus can perform a man-in-the-middle attack. This challenge patches that vulnerability by only allowing us to intercept the communication phase. - Since Alice sends Byron a
done!message afterFinish Handshakestep, we can recover the encrypted flag as follow:
- Send
done!to Byron -> Obtainwhat is the flag? I have the secret+ $s_B$ - Send
what is the flag? I have the secret+ $s_B$ to Alice -> Obtainthe flag is+ $s_A$
- Notice that when we send a message that starts with
the flag is, Byron only check whether the suffix matcheshkcert24{.*}, this means that bothhkcert24{MystizIsMyIdol}andhkcert24{}satisfy the regex. But how can we use this information up to our advantage? - Denote $KS$ as the keystream generated by AES-CTR, we have: $$ct = Enc(SK, pt) = KS \oplus pt$$$$Dec(SK, ct \oplus b) = KS \oplus ct \oplus b = pt \oplus b$$
- Utilizing this property, we can recover the flag byte-by-byte by just enumerating all 256 possibilities and checking when Byron replies with
nice flag!. - A problem here is that both
nice flag!andtoo bad...messages have same length, therefore we cannot distinguish those based on their length. To overcome this, we just need to forward the resonpse to Alice and observe the Alice’s response length, since the responses correspond with these 2 messages have different lengths.
Solve Script#
from pwnlib.tubes.remote import remote
import json
CONN = remote("c24b-pigeon-2.hkcert24.pwnable.hk", 1337, ssl=True)
alice_pubkey = eval(CONN.recvline().decode())["public_key"]
byron_pubkey = eval(CONN.recvline().decode())["public_key"]
done_ct = eval(CONN.recvline().decode())["ciphertext"]
CONN.sendlineafter('🕊️ '.encode(), b'byron ' + json.dumps({'type': 'communicate', 'ciphertext': done_ct}, separators=(',', ':')).encode())
secret_ct = eval(CONN.recvline().decode())["ciphertext"]
CONN.sendlineafter('🕊️ '.encode(), b'alice ' + json.dumps({'type': 'communicate', 'ciphertext': secret_ct}, separators=(',', ':')).encode())
flag_ct = bytes.fromhex(eval(CONN.recvline().decode())["ciphertext"])
known_len = len('the flag is hkcert24{')
flag = b'hkcert24{'
while known_len < len(flag_ct):
prefix = flag_ct[:known_len]
for b in range(256):
flag_ct_test = prefix + bytes([b])
CONN.sendlineafter('🕊️ '.encode(), b'byron ' + json.dumps({'type': 'communicate', 'ciphertext': flag_ct_test.hex()}, separators=(',', ':')).encode())
res_ct = eval(CONN.recvline().decode())["ciphertext"]
CONN.sendlineafter('🕊️ '.encode(), b'alice ' + json.dumps({'type': 'communicate', 'ciphertext': res_ct}, separators=(',', ':')).encode())
res_ct = eval(CONN.recvline().decode())["ciphertext"]
if len(res_ct) != 44:
flag += bytes([flag_ct[known_len] ^ b ^ ord('}')])
print(f'{flag = }')
known_len += 1
CONN.close()
FLAG: hkcert24{0n3_c4n_4ls0_l34k_1nf0rm4710n_fr0m_th3_l3n9th}
mAEStro (1): Sample#
Source Code#
Challenge Analysis#
- In this challenge, we are given a normal Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) implementation, except a “backdoor” that randomizes which operations are used for this AES based on $seed$.
- When connected, the server generates a secret key $K$ and secret message $m_0$ and gives us $c_0 = AES(K, m_0)$. With access to the encryption oracle, the target is to recover $m_0$.
Solution#
-
The AES includes 4 main operaions:
AddRoundKey: XOR-ing the state with round key,ShiftRows: Shift state’s rows,MixColumns: Mix bytes for each state’s column,SubBytes: Substitute one byte by another byte in SBox.
AES Structure (Source: CryptoHack)
-
However, only
AddRoundKeyinvolves the usage of secret key. Therefore, AES with noAddRoundKeyoperations can be easily reversed by applying the inverse functions ofShiftRows,SubBytesandMixColumns. -
This approach is feasible since
random.choicesis chosen with replacement, therefore we can bruteforce the $seed$ untilself.operationsdoes not containAddRoundKey. Then we implement thedecrypt_blockmethod for the custom AES to recover $m_0$ and get the flag.
Solve Script#
from aes import *
from pwnlib.tubes.remote import remote
def decrypt_block(self, ciphertext):
assert len(ciphertext) == 16
cipher_state = bytes2matrix(ciphertext)
for operation, *args in self.operations[::-1]:
if operation == shift_rows:
inv_shift_rows(cipher_state, *args)
elif operation == sub_bytes:
inv_sub_bytes(cipher_state, *args)
elif operation == mix_columns:
inv_mix_columns(cipher_state, *args)
else:
print("Error")
return matrix2bytes(cipher_state)
AES.decrypt_block = decrypt_block
CONN = remote("c06a-maestro-1.hkcert24.pwnable.hk", 1337, ssl=True)
seed = b'\xdc\xc2\xad\xd2Q\x117\x83I\x98\xa1\xe3\xdd[\x92\x8e'
CONN.sendlineafter('🌱 '.encode(), seed.hex().encode())
cipher = AES(b"\x00" * 32, seed)
c0 = CONN.recvline().decode().strip().split(' ')[-1]
m0 = cipher.decrypt_block(bytes.fromhex(c0))
print(f'{m0 = }')
CONN.sendlineafter('💬 '.encode(), m0.hex().encode())
CONN.interactive()
FLAG: hkcert24{a3s_i5_k3yl3ss_1f_th3re_ar3_n0_4ddr0undk3y_op3r4t10ns}
mAEStro (2): Shuffle#
Challenge Analysis#
- This challenge setup is the same as
mAEStro (1): Sample, butrandom.shuffleis used instead ofrandom.choicesin the backdoor function. The target remains the same, recover $m_0$ given its ciphertext $c_0$ and access to encryption oracle.
Solution#
- The use of
random.shufflebeats the approach ofmAEStro (1): Samplebecause now all the operations of original AES must be taken. - Among 4 aforementioned AES’s operations, only
SubBytesprovides non-linearity to the ciphertext. The other operations can be expressed as affine transformation, i.e. applying operation $\mathcal{O}$ on the state $S$ will yield the result $S’ = P_\mathcal{O} * S + K_\mathcal{O}$ where $P_\mathcal{O} \in Z_2^{128 \times 128}$; $S, S’, K_\mathcal{O} \in Z_2^{128 \times 1}$; $P_\mathcal{O}$ is a constant with respective to $\mathcal{O}$; $K_\mathcal{O}$ is constant and dependent on key in case ofAddRoundKey. - Since we are working in $GF(2)$, suppose we have $S_0’, S_1’, S_2’$ as the results of applying affine transformation $\mathcal{O}$ on $S_0, S_1, S_2$: $$S_0’ = P_\mathcal{O} * S_0 + K_\mathcal{O}$$ $$S_1’ = P_\mathcal{O} * S_1 + K_\mathcal{O}$$ $$S_2’ = P_\mathcal{O} * S_2 + K_\mathcal{O}$$ $$\Rightarrow S’ = S_0’ + S_1’ + S_2’ = P_\mathcal{O} * (S_0 + S_1 + S_2) + K_\mathcal{O} = P_\mathcal{O} * S + K_\mathcal{O}$$
- Therefore, we can obtain the result $S’$ of applying operation $\mathcal{O}$ on $S = \sum_{i = 0}^{2 * n - 1}{S_i}$ by evaluating $P_\mathcal{O}* \sum_{i = 0}^{2 * n - 1}{S_i} + K_\mathcal{O}$
- Back to the challenge, let’s consider a simplified version of AES with only 3
AddRoundKeyoperations. If we can remove all theSubBytesbetweenAddRoundKeyoperations, e.g. like the figure below, then we can express $S_6$ as the result of an affine transformation on $S_1$. Since we are given $S$ and $S’$ (plaintext and ciphertext, respectively) and both the paths from $S$ to $S_1$ and $S’$ to $S_6$ do not involve key, calculating $S_1$ and $S_6$ is feasible.
Simplified AES - If we can gather multiple plaintext-ciphertext ($m_i - c_i$) pairs, we can express the original ciphertext $c_0$ in terms of $c_i$ by solving a system of linear equations over $GF(2)$, then applying the homomorphic properties above to extract the output of AES before the first
AddRoundKeyoperation. And then easy flag!!!
Solve Script#
from sage.all import *
from pwnlib.util.fiddling import xor
from pwnlib.tubes.remote import remote
from aes import *
import os
def bytes2bits(b):
return list(map(int, ''.join(format(x, '08b') for x in b)))
def encrypt_block(self, plaintext, start = None, end = None):
"""
Encrypts a single block of 16 byte long plaintext.
"""
assert len(plaintext) == 16
plain_state = bytes2matrix(plaintext)
if not start:
start = 0
if not end:
end = len(self.operations)
for operation, *args in self.operations[start:end]:
operation(plain_state, *args)
return matrix2bytes(plain_state)
def decrypt_block(self, ciphertext, start = None, end = None):
assert len(ciphertext) == 16
cipher_state = bytes2matrix(ciphertext)
if not end:
end = len(self.operations)
for operation, *args in self.operations[end:start:-1]:
if operation == add_round_key:
add_round_key(cipher_state, *args)
elif operation == shift_rows:
inv_shift_rows(cipher_state, *args)
elif operation == sub_bytes:
inv_sub_bytes(cipher_state, *args)
elif operation == mix_columns:
inv_mix_columns(cipher_state, *args)
else:
print("Error", operation)
return matrix2bytes(cipher_state)
AES.encrypt_block = encrypt_block
AES.decrypt_block = decrypt_block
K = GF(2)
SIZE = 150
seed = b'{\xe3\x95\xc5C`\xc3R\xda\xa0\xb0\x85+\xa2\xda3\xec\xac$\x11\xbaoBM\xa2GV\x12t\xcb\xbf/\x8f\x93N\x84\xcdiF\xa3w\x03\xecS\xad\xd7\xa7\x9e\xc1\x82\x83Ab#\xb8a}\xcaf\xa9C\x827E'
cipher = AES(b"\x00" * 32, seed = seed)
pts = [os.urandom(16) for _ in range(SIZE)]
cts = []
cts_start = [cipher.encrypt_block(pt, end = 19) for pt in pts]
CONN = remote("c06b-maestro-2.hkcert24.pwnable.hk", 1337, ssl=True)
CONN.sendlineafter('🌱 '.encode(), seed.hex().encode())
c0 = bytes.fromhex(CONN.recvline().decode().strip().split(' ')[-1])
for pt in pts:
CONN.sendlineafter('💬 '.encode(), pt.hex().encode())
cts.append(bytes.fromhex(CONN.recvline().decode().strip().split(' ')[-1]))
cts_end = [cipher.decrypt_block(ct, start = -17) for ct in cts]
lhs = Matrix(K, [bytes2bits(cts_end[i]) for i in range(SIZE)]).T
lhs = lhs.stack(vector(K, [1 for _ in range(SIZE)]))
rhs = Matrix(K, bytes2bits(cipher.decrypt_block(c0, start = -17)) + [1]).T
res = lhs.solve_right(rhs).list()
start = b'\x00' * 16
for i in range(len(res)):
if res[i]:
start = xor(start, cts_start[i])
m0 = cipher.decrypt_block(start, end = 18)
print(f'{m0 = }')
CONN.sendlineafter('💬 '.encode(), m0.hex().encode())
CONN.interactive()
FLAG: hkcert24{m1xc0lumn5_1s_th3_0nly_0p3r4t10n_th4t_m4ps_0n3_by73s_t0_mult16l3_by73s}